Short Biography
Naoki KIMURA is a 3rd-year Ph.D. student at The University of Tokyo, advised by Prof. Jun Rekimoto and Thad Starner at Georgia Tech. His research focuses on machine learning for human-computer interaction, through 1) silent speech interaction for wearable devices, 2) Deep generative models for enhancing immersive experiences.
Ph.D. Fellow@GoogleAI, Ph.D. Fellow@Microsoft Research, D-CORE@Microsoft Research, ACT-X, PFN intern 2018
Education
-
2019 - Ph.D. student in Applied Computer Science
The University of Tokyo, Japan.
Supervisor: Prof. Jun Rekimoto -
2017 - 2019 Master of Applied Computer Science
The University of Tokyo, Japan.
Supervisor: Prof. Jun Rekimoto -
2013 - 2019 Bachelor of Urban Engineering
The University of Tokyo
Research Projects
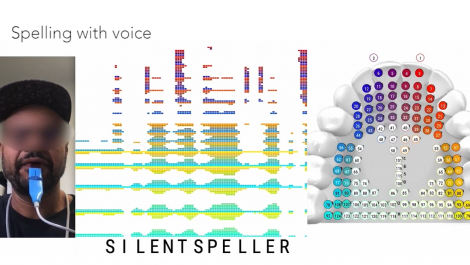
SilentSpeller: Towards mobile, hands-free, silent speech text entry using electropalatography
Naoki Kimura, Tan Gemicioglu, Jonathan Womack, Richard Li, Yuhui Zhao, Abdelkareem Bedri, Zixiong Su, Alex Olwal, Jun Rekimoto, Thad Starner
[Demo-VIDEO] [Demo-PDF 2020 ver.]
To appear @CHI2022 as a full paper
Voice control provides hands-free access to computing, but there are many situations where audible speech is not appropriate. Most unvoiced speech text entry systems cannot be used while on-the-go due to movement artifacts. SilentSpeller enables mobile silent texting using a dental retainer with capacitive touch sensors to track tongue movement. Users type by spelling words without voicing. In offline isolated word testing on a 1164-word dictionary, SilentSpeller achieves an average 97\% character accuracy. Walking seems to have little effect on recognition accuracy; average offline character accuracy was roughly equivalent on 107 phrases entered while walking (97.5%) or seated (96.5%). To demonstrate extensibility, the system was tested on 100 unseen words, leading to an average 94% accuracy. Live text entry speeds for seven participants averaged 37 words per minute at 87% accuracy. Comparing silent spelling to current practice suggests that SilentSpeller may be a viable alternative for silent mobile text entry.
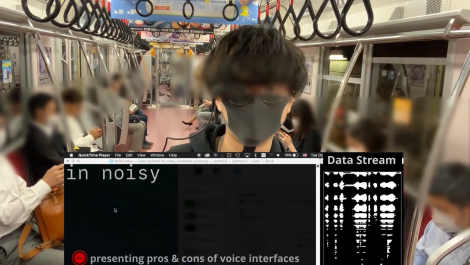
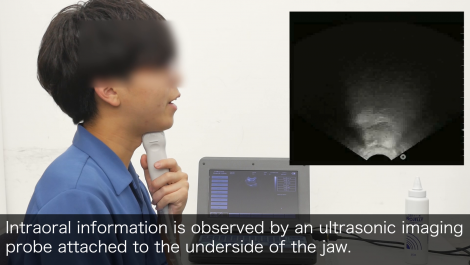
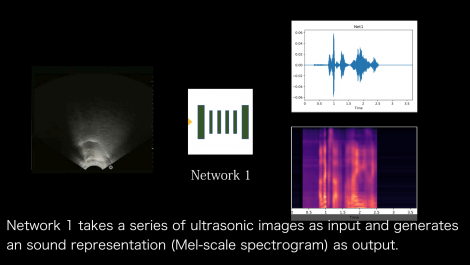
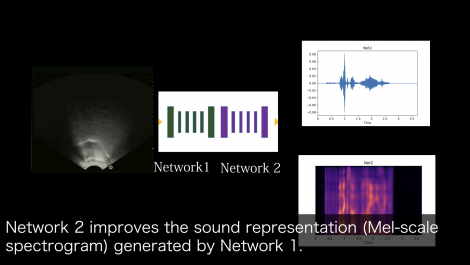
SottoVoce: An Ultrasound Imaging-Based Silent Speech Interaction Using Deep Neural Networks
Naoki Kimura, Michinari Kono, Jun Rekimoto
🏅Honorable Mention Award @CHI2019
The availability of digital devices operated by voice is rapidly expanding. However, the usage situation of voice interfaces is still restricted. For example, speaking in public places becomes an annoyance to surrounding people, and secret information should not be uttered. Environmental noise may reduce the accuracy of the speech recognition. To address these limitations, SottoVoce detects a user’s unuttered voice. From internal information observed by an ultrasonic imaging sensor attached to the underside of the jaw, our proposed system recognizes the utterance contents without the user actually uttering voice. Our proposed deep neural network model is used to obtain acoustic features from a sequence of ultrasound images. We confirmed that audio signals generated by our system can control existing smart speakers. We also observed that a user can adjust their oral movement to learn and improve accuracy of their voice recognition.
ExtVision: Augmentation of Visual Experiences with Generation of Context Images for Peripheral Vision Using Deep Neural Network
Naoki Kimura, Jun Rekimoto
🏅Honorable Mention Award @CHI2018
We propose a system, called ExtVision, to augment visual experiences by generating and projecting context-images onto the periphery of the television or computer screen. A peripheral projection of the context-image is one of the most effective techniques to enhance visual experiences. However, the projection is not commonly used at present, because of the difficulty in preparing the context-image. In this paper, we propose a deep neural network-based method to generate context-images for peripheral projection. A user study was performed to investigate the manner in which the proposed system augments traditional visual experiences. In addition, we present applications and future prospects of the developed system.
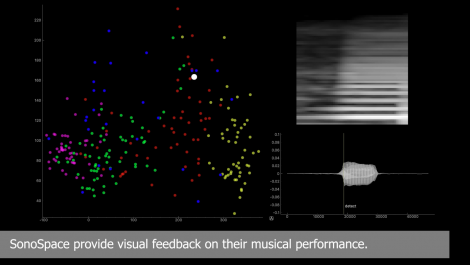
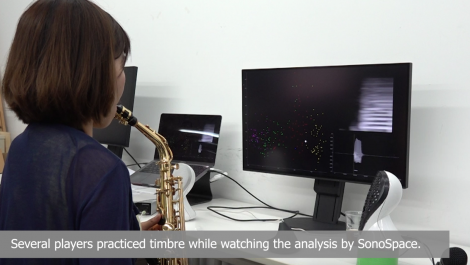
SonoSpace: Visual Feedback of Timbre with Unsupervised Learning
Accepted as Oral @ACMMM2020
One of the most difficult things in practicing musical instruments is improving timbre. Unlike pitch and rhythm, timbre is a high-dimensional and sensuous concept, and learners cannot evaluate their timbre by themselves. To efficiently improve their timbre control, learners generally need a teacher to provide feedback about timbre. However, hiring teachers is often expensive and sometimes difficult. Our goal is to develop a low-cost learning system that substitutes the teacher. We found that a variational autoencoder (VAE), which is an unsupervised neural network model, provides a 2-dimensional user-friendly mapping of timbre. Our system, SonoSpace, maps the learner’s timbre into a 2D latent space extracted from an advanced player’s performance. Seeing this 2D latent space, the learner can visually grasp the relative distance between their timbre and that of the advanced player. Although our system was evaluated mainly with an alto saxophone, SonoSpace could also be applied to other instruments, such as trumpets, flutes, and drums.
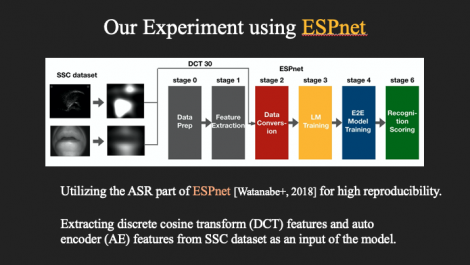
End-to-End Deep Learning Speech Recognition Model for Silent Speech Challenge
Naoki Kimura, Zixiong Su, Takaaki Saeki
Show-and-Tell @INTERSPEECH2020
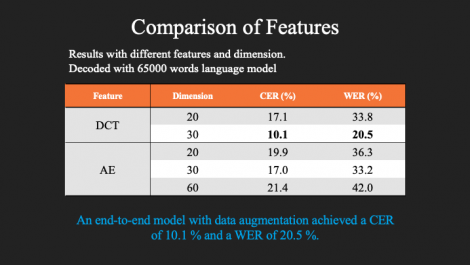
This work is the first attempt to apply an end-to-end, deep neural network-based automatic speech recognition (ASR) pipeline to the Silent Speech Challenge dataset (SSC), which contains synchronized ultrasound images and lip images captured when a single speaker read the TIMIT corpus without uttering audible sounds. In silent speech research using the SSC dataset, established methods in ASR have been utilized with some modifications to use it in visual speech recognition. In this work, we tested the SOTA method of ASR on the SSC dataset using the End-to-End Speech Processing Toolkit, ESPnet. The experimental results show that this end-to-end method achieved a character error rate (CER) of 10.1% and a WER of 20.5% by incorporating SpecAugment, demonstrating the possibility to further improve the performance with additional data collection.
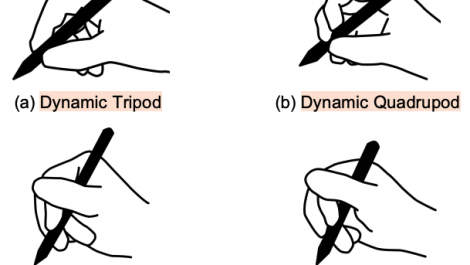
Elicitation of Alternative Pen-Holding Postures for Quick Action Triggers with Suitability for EMG Armband Detection
Fabrice Matulic, Brian Vogel, Naoki Kimura and Daniel Vogel.
@ISS2019
In this project we study what alternative ways of gripping a digital pen people might choose to trigger actions and shortcuts in applications (e.g. while holding the pen, extend the pinkie to invoke a menu). We also investigate how well we can recognise these different pen-holding postures using data collected from an EMG armband and deep learning.
Deep Dive: Deep-Neural-Network-Based Video Extension for Immersive Head-Mounted Display Experiences
Naoki Kimura, Michinari Kono, Jun Rekimoto
[VIDEO]
Accepted @PerDis2019
Immersion is an important factor in video experiences. Therefore, various methods and video viewing systems have been proposed. Head-mounted displays (HMDs) are home-friendly pervasive devices, which can provide an immersive video experience owing to their wide field-of-view (FoV) and separation of users from the outside environment. They are often used for viewing panoramic and stereoscopic recorded videos or virtually generated environments, but the demand for viewing standard plane videos with HMDs has increased. However, the theater mode, which restricts the FoV, is basically used for viewing plane videos. Thus, the advantages of HMDs are not fully utilized. Therefore, we explored a method for viewing plane videos by an HMD, in combination with view augmentation by LED implants to the HMD.We have constructed a system for viewing plane videos using an HMD with a deep neural network (DNN) model optimized for generating and extending images for peripheral vision and wide FoV customization. We found that enlarging the original video and extending the video with our DNN model can improve the user experience. However, our method provided more comfortable viewing by preventing motion sickness in a first-person-view video.
Selected Awards
-
2020 Microsoft Research Asia Fellowship
Fellowship
-
2019 Google PhD Fellowship
Fellowship
-
2019 Best Paper Honorable Mention Award @ CHI2019
SottoVoce: An Ultrasound Imaging-Based Silent Speech Interaction Using Deep Neural Networks
-
2018 Best Paper Honorable Mention Award @ CHI2018
ExtVision: Augmentation of Visual Experiences with Generation of Context Images for Peripheral Vision Using Deep Neural Network
-
2019 Best Master Thesis Award @ The University Of Tokyo
The content goes here...
-
2019 UTokyo - TOYOTA Study Abroad Scholarships (5,000,000 Yen)
The content goes here...
-
2019 Nominee of President’s Award of the University of Tokyo
The content goes here...
-
2019 KUMA FOUNDATION Creator Scholarship (1,200,000 Yen)
The content goes here...
-
2019 TOYOTA/Dwango AI Scholarship (1,200,000 yen)
The content goes here...
-
2018 TOYOTA/Dwango AI Scholarship (1,200,000 yen)
The content goes here...
-
2018 37th and 38th Leave a Nest Research Awards (1,500,000 yen)
The content goes here...
Selected Publications
I am text block. Click edit button to change this text. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.